HEXAZINONE
Common name: Hexazinone
Chemical name: 3-cyclohexyl-6-dimethylamino-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione
CAS No:
Empirical formula:C12H20N4O2
Molecular weight:
Structural formula: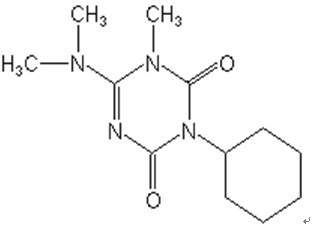
Activity: Triazinone herbicide
Physical & Chemical Properties:
Appearance:Pale yellow crystalline powder
Color:Pale yellow
Odour: Odorless
Density at 200C: 1.37g/cm3
Vapour pressure at 20/250C: 2.7×10-3Pa
Volatility: Minimal, it does not volatilize readily when applied in the field. The potential to volatilize, however, increases with increasing temperature, increasing soil moisture, and decreasing clay and organic matter content.
Hydrolysis DT50…….Days……. 0C……pH: No detectable hydrolysis after 30 days at 25°C and pH 5, 7 or 9; average over several Ph levels at 15℃: >56 days.
Photolysis: Photolytically stable at pH 7 and 25°C
Solubility: water--29.8-33g/l at 25°C at pH 7-9
Solubility organic solvents, 25°C: Chloroform-3880g/kg; methanol-2650g/kg; DMF-863g/kg; acetone-790g/kg; benzene-940g/kg; toluene-386g/kg; hexane-3g/kg.
n-octanol/water partition coefficient: log Pow= 1.2 at 25°C and pH 7
Melting point 0C: 115-117℃
Application: Hexazinone is a triazinone herbicide used against many annual, biennial, and perennial weeds, as well as some woody plants. It is mostly used on non-crop areas; however, it is used selectively for the control of weeds among sugar cane, pineapples, and lucerne. Hexazinone is a systemic herbicide that works by inhibiting photosynthesis in the target plants.
It’s a herbicide used to control a broad spectrum of weeds including undesirable woody plants in alfalfa, rangeland and pasture, woodland, pineapples, sugarcane and blueberries. It is also used on ornamental plants, forest trees and other non-crop areas. Hexazinone is registered for pre-emergent, post-emergence, layby, directed spray and basal soil applications. It is used as a non-selective herbicide in non-cropland areas and as a selective herbicide in reforestation practices.
