DIFLUFENICAN
Common Name: Diflufenican
Chemical name: N-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-[(3-trifluoromethyl)phenoxy] nicotinanilide
Physical appearance: off-white to white crystalline powder
Cas Nº: 83164-33-4
Empirical formula: C16H11F5N2O2
Structural formula:
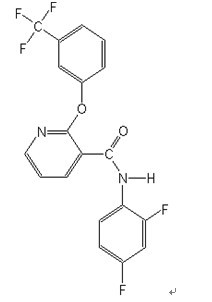
Molecular weight: 394.3
Activity: anilide herbicide, pyridine herbicide
- Identity: Diflufenican (ISO)
- Physical state: colour, appearance, odour, etc.:
Diflufenican is off-white to white crystalline powder, odourless.
- Melting, boiling and descomposition point.:
Melting point: 162.5℃
Boiling point: not available.
Decomposition point: not available.
- Vapour pressure: 7.07×10-5Pa(30℃)
- Solubility in water and other solvents: (25℃): acetone: 100g/L; DMF: 100g/L;
xylene: 20g/L; cyclohexane: 10g/L; Water: 0.05mg/L.
- Coefficient of partition between water and an appropriate non-miscible solvent.:
Octanol/Water: Log Pow=4.2
- Flammability.: Diflufenican technical material if of crystalline powder, it’s inflammable
at normal conditions.
- Explosive and corrosive properties: Diflufenican technical material is of crylstalline
powder form, it’s not explosive and corrosive at normal conditions.
- Specific gravity: 1.15g/cm3, 25℃
- Hidrolysis measure:
Diflufenican is highly persistent in the soil with dissipation DT50 values of 311 to 733
days, as well as in the water body with little hydrolysis over a range of pH levels at 22℃.
This could lead to prolonged contamination of water due to run-off of soil containing
residues and through direct contamination of water by over-spray or spray drift.
- Photolysis measure:
Diflufenican is of Soil DT50 15 to 30 weeks. Stable to hydrolysis (25℃) at pH 5, pH 7
and pH 9. Fairly stable to photolysis.
- Absorption spectrum: not available.
- Storage stability: Diflufenican is stable at normal conditions, it is stable for at least 24
month since production at original sealed package in low temperature area.
Application: Diflufenican blocks carotenoid biosynthesis, by inhibition of phytoene desaturase. Mode of action Selective contact and residual herbicide, absorbed principally by the shoots of germinating seedlings, with limited translocation. Uses Applied at 125-250 g/ha pre- or early post-emergence in autumn-sown wheat and barley, to control grass and broad-leaved weeds, particularly Galium, Veronica and Viola spp. Normally used in combination with isoproturon or other cereal herbicides. Phytotoxicity Any slight phytotoxicity is in the form of small transient patches on basal leaves, with no adverse effect on crop development. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected tradenames: 'Fenican' (Aventis); 'Tigrex' (Aventis); mixtures: 'Bacara' ( flurtamone) (Aventis); 'Javelin' ( isoproturon) (Aventis).

