Dinotefuran
Name: Dinotefuran
Other name: (RS)-1-Methyl-2-nitro-3-(tetrahydro-3-furylmethyl) guanidine; MTI-446
Chemical name: 2-Methyl-1-nitro-3-(tetrahydrofuran-3-ylmethyl)guanidine
CAS No: 165252-70-0
Empirical formula: C7H14N4O3
Molecular weight: 202.21
Structural formula: 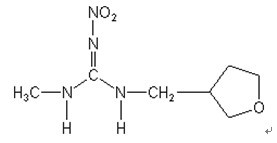
Physical & Chemical Properties:
Appearance: grayish-white to white powder
Melting point: 107.5℃;
Water solubility: 39.83g/l.
Solubility in organic solvent: Dinotefuran is highly soluble in dichloromethane, acetone, methanol, and ethyl acetate.
Log Pow of -0.549 at 25o C
vapor pressure: <1.7 x 10-6 Pa at 25o C
Stability: Dinotefuran is stable at normal storage condition, it’s non-flammable, is not explosive to thermal, shock and frictional tests
Application: Dinotefuran is nitroguanidine neonicotinoid insecticide for control of insect pests such as aphids, whiteflies, thrips, leafhoppers, leafminers, sawflies, mole cricket, white grubs, lacebugs, billbugs, beetles, mealybugs, and cockroaches on leafy vegetables, in residential and commercial buildings, and for professional turf management. Its mechanism of action involves disruption of the insect's nervous system by inhibiting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, it acts through contact and ingestion and results in the cessation of feeding within several hours of contact and death shortly after. Dinotefuran does not inhibit cholinesterase or interfere with sodium channels. Therefore, its mode of action is different from those of organophosphate, carbamate, and pyrethroid compounds. It appears that Dinotefuran acts as an agonist of insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, but it is postulated that Dinotefuran affects the nicotinic acetylcholine binding in a mode that differs from other neonicotinoid insecticides. It is reported that Dinotefuran was highly active on a certain silverleaf whitefly strain which developed resistance against imidacloprid.
Products available: Dinotefuran 93%min tech, 20% WP
Packing: 25kg fiber drum.

